How to Calculate Direct Labor Variances
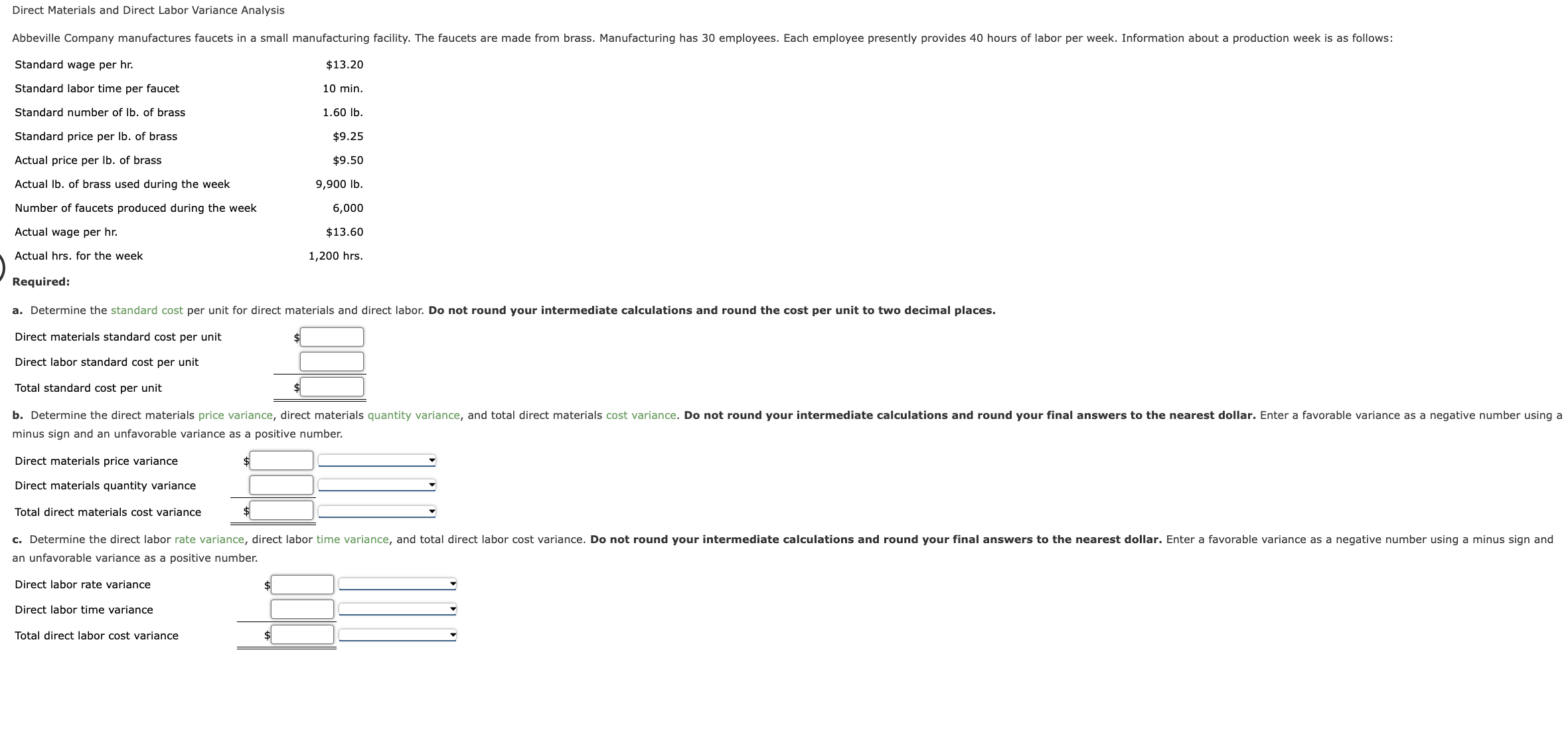
Thus positive values of direct labor rate variance as calculated above, are favorable and negative values are unfavorable. In this question, the company has experienced an unfavorable direct labor efficiency variance of $325 during March because its workers took more hours (1,850) than the hours allowed by standards (1,800) to complete 600 units. Usually, direct labor rate variance does not occur due to change in labor rates because they are normally pretty easy to predict. A common reason of unfavorable labor rate variance is an inappropriate/inefficient use of direct labor workers by production supervisors. During June 2022, Bright Company’s workers worked for 450 hours to manufacture 180 units of finished product.
Submit to get your question answered.
Recall from Figure 10.1 that the standard rate for Jerry’s is$13 per direct labor hour and the standard direct labor hours is0.10 per unit. Figure 10.6 shows how to calculate the labor rateand efficiency variances given the actual results and standardsinformation. Review this figure carefully before moving on to thenext section where these calculations are explained in detail.
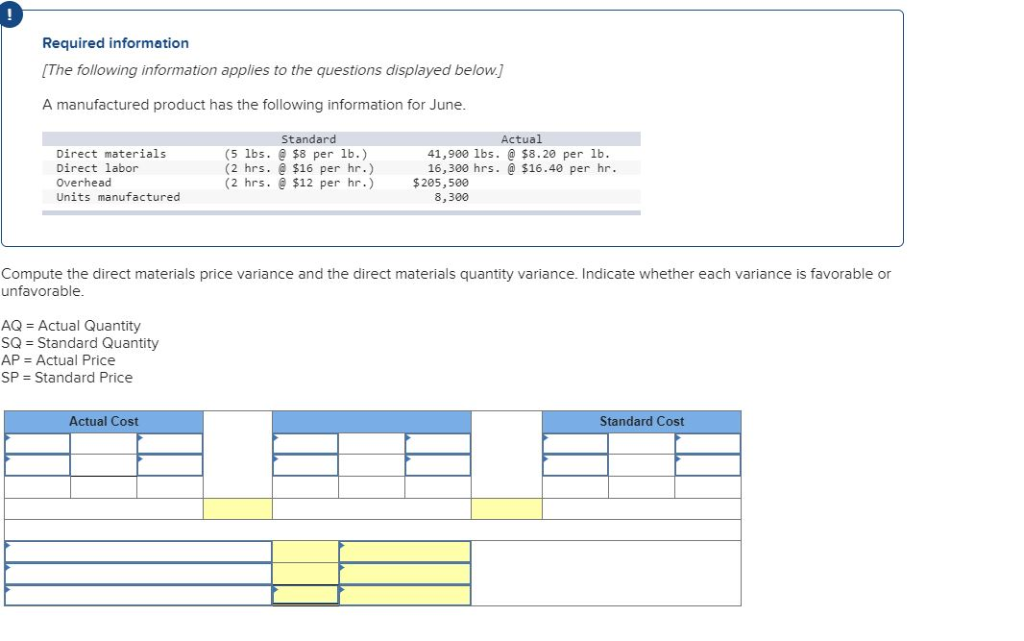
Fundamentals of Direct Labor Variances
On the other hand, if workers take an amount of time that is more than the amount of time allowed by standards, the variance is known as unfavorable direct labor efficiency variance. In this case, the actual rate per hour is $7.50, the standard rate per hour is $8.00, and the actual hour worked is 0.10 hours per box. This is a favorable outcome because the actual rate of pay was less than the standard rate of pay. As a result of this favorable outcome information, the company may consider continuing operations as they exist, or could change future budget projections to reflect higher profit margins, among other things.
Labor Efficiency Variance
He represents clients before the IRS and state taxing authorities concerning audits, tax controversies, and offers in compromise. He has served in various leadership roles in the American Bar Association and as Great Lakes Area liaison with the IRS. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
He is a four-time Dummies book author, a blogger, and a video host on accounting and finance topics. As mentioned earlier, the cause of one variance might influenceanother variance. For example, many of the explanations shown inFigure 10.7 might also apply to the favorable materials quantityvariance. An overview of these two types of labor efficiency variance is given below. Daniel S. Welytok, JD, LLM, is a partner in the business practice group of Whyte Hirschboeck Dudek S.C., where he concentrates in the areas of taxation and business law. Dan advises clients on strategic planning, federal and state tax issues, transactional matters, and employee benefits.
If the actual rate of pay per hour is less than the standard rate of pay per hour, the variance will be a favorable variance. If, however, the actual rate of pay per hour is greater than the standard rate of pay per hour, the variance will be unfavorable. With either of these formulas, the actual rate per hour refers to the actual rate of pay for workers to create one unit of product. The standard rate per hour is the expected rate of pay for workers to create one unit of product. The actual hours worked are the actual number of hours worked to create one unit of product. If there is no difference between the standard rate and the actual rate, the outcome will be zero, and no variance exists.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education which of the following is the formula to compute the direct labor rate variance organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
The standard direct labor rate was set at $5.60 per hour but the direct labor workers were actually paid at a rate of $5.40 per hour. Find the direct labor rate variance of Bright Company for the month of June. Figure 8.4 shows the connection between the direct labor rate variance and direct labor time variance to total direct labor variance. The direct labor variance measures how efficiently the company uses labor as well as how effective it is at pricing labor. There are two components to a labor variance, the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor time variance.
- As a result of this favorable outcome information, the company may consider continuing operations as they exist, or could change future budget projections to reflect higher profit margins, among other things.
- An example is when a highly paid worker performs a low-level task, which influences labor efficiency variance.
- In this case, the actual hours worked per box are 0.20, the standard hours per box are 0.10, and the standard rate per hour is $8.00.
- Direct labor rate variance (also called direct labor price or spending variance) is the difference between the total cost of direct labor at standard cost (i.e. direct labor hours at standard rate) and the actual direct labor cost.
- An adverse labor rate variance indicates higher labor costs incurred during a period compared with the standard.
- In such situations, a better idea may be to dispense with direct labor efficiency variance – at least for the sake of workers’ motivation at factory floor.
In order to keep the overall direct labor cost inline with standards while maintaining the output quality, it is much important to assign right tasks to right workers. Like direct labor rate variance, this variance may be favorable or unfavorable. If workers manufacture a certain number of units in an amount of time that is less than the amount of time allowed by standards for that number of units, the variance is known as favorable direct labor efficiency variance.
To compute the direct labor quantity variance, subtract the standard cost of direct labor ($48,000) from the actual hours of direct labor at standard rate ($43,200). This math results in a favorable variance of $4,800, indicating that the company saves $4,800 in expenses because its employees work 400 fewer hours than expected. All tasks do not require equally skilled workers; some tasks are more complicated and require more experienced workers than others.
If the outcome is unfavorable, the actual costs related to labor were more than the expected (standard) costs. If the outcome is favorable, the actual costs related to labor are less than the expected (standard) costs. Note that both approaches—the direct labor efficiency variancecalculation and the alternative calculation—yield the sameresult. Direct Labor Rate Variance is the measure of difference between the actual cost of direct labor and the standard cost of direct labor utilized during a period.

0 comments