8 3 Compute and Evaluate Labor Variances Principles of Accounting, Volume 2: Managerial Accounting
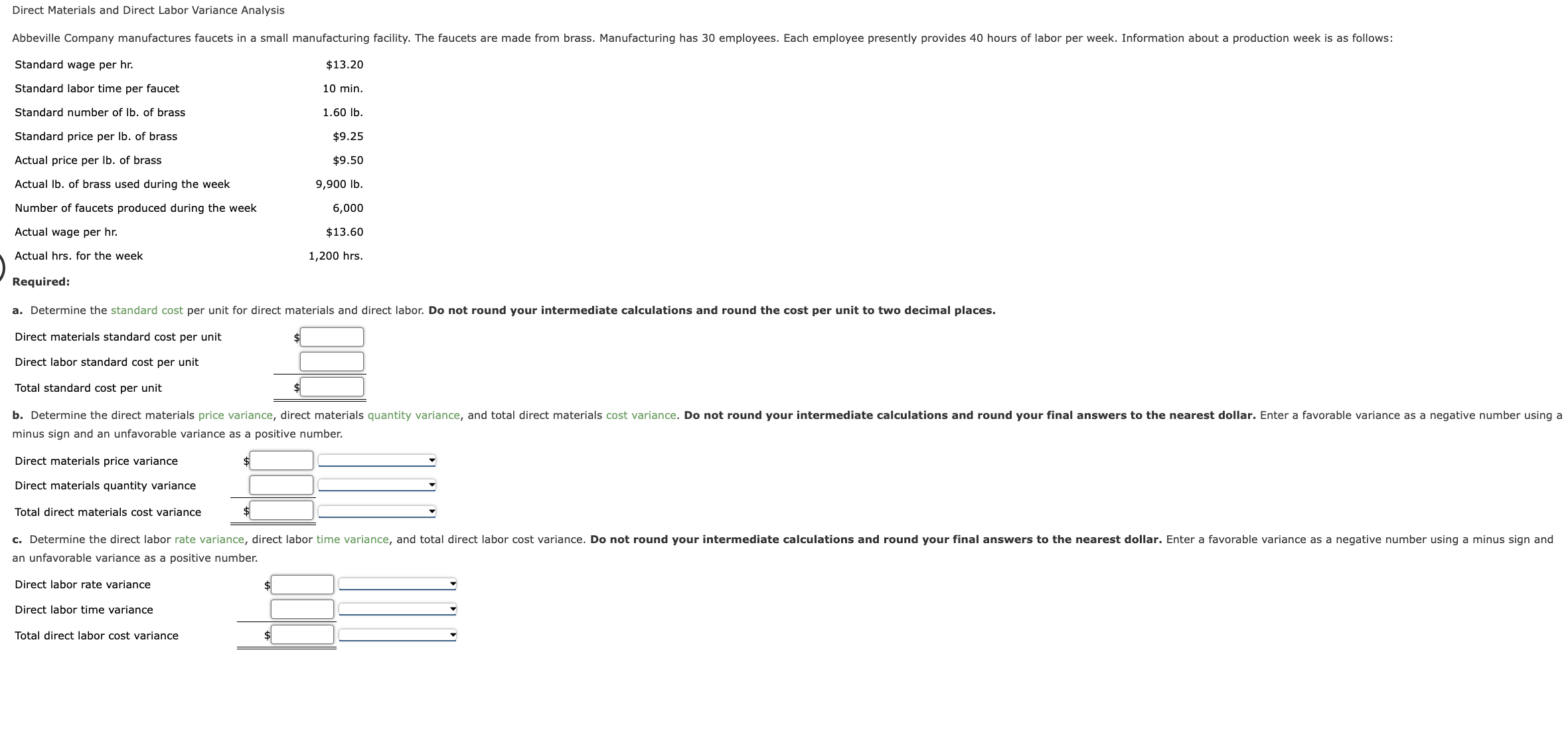
The most common causes of labor variances are changes in employee skills, supervision, production methods capabilities and tools. An example is when a highly paid worker performs a low-level task, which influences labor efficiency which of the following is the formula to compute the direct labor rate variance variance. Figure 10.7 contains some possible explanations for the laborrate variance (left panel) and labor efficiency variance (rightpanel). Kenneth W. Boyd has 30 years of experience in accounting and financial services.
Labor Efficiency Variance
The first option is not in line with just in time (JIT) principle which focuses on minimizing all types of inventories. Excessive inventories, particularly those that are still in process, are considered evil as they generally cause additional storage cost, high defect rates and spoil workers’ efficiency. Due to these reasons, managers need to be cautious in using this variance, particularly when the workers’ team is fixed in short run. In such situations, a better idea may be to dispense with direct labor efficiency variance – at least for the sake of workers’ motivation at factory floor. This information gives the management a way tomonitor and control production costs.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
- As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider retraining its workers, changing the production process to be more efficient, or increasing prices to cover labor costs.
- Michellewas asked to find out why direct labor and direct materials costswere higher than budgeted, even after factoring in the 5 percentincrease in sales over the initial budget.
- Direct labor rate variance is very similar in concept to direct material price variance.
- This is an unfavorable outcome because the actual hours worked were more than the standard hours expected per box.
- This is a favorable outcome because the actual rate of pay was less than the standard rate of pay.
- Hitech manufacturing company is highly labor intensive and uses standard costing system.
A direct labor variance is caused by differences in either wage rates or hours worked. As with direct materials variances, you can use either formulas or a diagram to compute direct labor variances. Doctors, for example, have a time allotment for a physical exam and base their fee on the expected time.
5: Direct Labor Variance Analysis
After filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy inDecember 2002, United cut close to $5,000,000,000in annual expenditures. As a result of these cost cuts, United wasable to emerge from bankruptcy in 2006. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License . Mark P. Holtzman, PhD, CPA, is Chair of the Department of Accounting and Taxation at Seton Hall University. He has taught accounting at the college level for 17 years and runs the Accountinator website at , which gives practical accounting advice to entrepreneurs.
Direct Labor Variances FAQs
An adverse labor rate variance indicates higher labor costs incurred during a period compared with the standard. The combination of the two variances can produce one overall total direct labor cost variance. Because Band made 1,000 cases of books this year, employees should have worked 4,000 hours (1,000 cases x 4 hours per case). However, employees actually worked 3,600 hours, for which they were paid an average of $13 per hour. Other reasons of labor rate variance include the payment of overtime premium to workers in case of rush orders with aggressive delivery dates and relying on inaccurate or incomplete data at the time of setting direct labor standards.
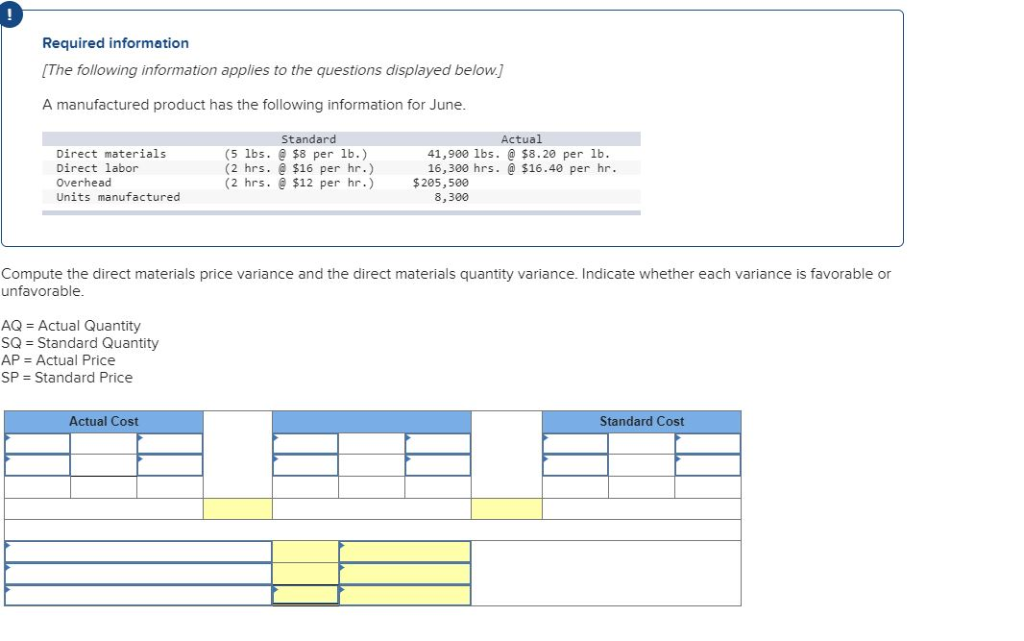
The pay cut was proposed to last as long as the companyremained in bankruptcy and was expected to provide savings ofapproximately $620,000,000. How would this unforeseen pay cutaffect United’s direct labor rate variance? Thedirect labor rate variance would likely be favorable, perhapstotaling close to $620,000,000, depending on how much of thesesavings management anticipated when the budget was firstestablished. In this example, the Hitech company has an unfavorable labor rate variance of $90 because it has paid a higher hourly rate ($7.95) than the standard hourly rate ($7.80).
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
In this case, the actual hours worked per box are 0.20, the standard hours per box are 0.10, and the standard rate per hour is $8.00. This is an unfavorable outcome because the actual hours worked were more than the standard hours expected per box. As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider retraining its workers, changing the production process to be more efficient, or increasing prices to cover labor costs. In this case, the actual rate per hour is $9.50, the standard rate per hour is $8.00, and the actual hours worked per box are 0.10 hours. This is an unfavorable outcome because the actual rate per hour was more than the standard rate per hour.
The difference between the standard cost of direct labor and the actual hours of direct labor at standard rate equals the direct labor quantity variance. The direct labor efficiency variance may be computed either in hours or in dollars. Suppose, for example, the standard time to manufacture a product is one hour but the product is completed in 1.15 hours, the variance in hours would be 0.15 hours – unfavorable. If the direct labor cost is $6.00 per hour, the variance in dollars would be $0.90 (0.15 hours × $6.00). For proper financial measurement, the variance is normally expressed in dollars rather than hours. The total direct labor variance is also found by combining the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor time variance.
It is defined as the differencebetween the actual number of direct labor hours worked and budgeteddirect labor hours that should have been worked based on thestandards. To compute the direct labor price variance, subtract the actual hours of direct labor at standard rate ($43,200) from the actual cost of direct labor ($46,800) to get a $3,600 unfavorable variance. This result means the company incurs an additional $3,600 in expense by paying its employees an average of $13 per hour rather than $12. In other words, when actual number of hours worked differ from the standard number of hours allowed to manufacture a certain number of units, labor efficiency variance occurs. Hitech manufacturing company is highly labor intensive and uses standard costing system. The standard time to manufacture a product at Hitech is 2.5 direct labor hours.

0 comments